我院教师在《Agricultural Water Management》发表最新研究成果
作者:发布时间:2021-12-30浏览次数:1050
北京时间2月1日,我院农业水利工程专业柏宇老师作为第一兼通讯作者在《Agricultural Water Management》发表了最新研究成果,文章标题为《Optimization of the nitrogen fertilizer schedule of maize under drip irrigation in Jilin, China, based on DSSAT and GA》(中译:基于DSSAT模型和GA算法优化吉林省玉米滴灌氮肥施用制度),揭示了吉林省玉米水肥耦合作用下氮肥的优化施用机理。(文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106555)
玉米是我国的主要农作物之一,提高玉米产量有利于保障我国的粮食安全,所以如何结合现有技术优化农田氮肥施用制度是当前的一个热门话题。本研究以吉林省中部地区为研究对象,进行了为期三年(2014-2016)的田间试验(2014年的数据用于校准DSSAT模型,2015年的数据用于验证DSSAT模型,2016年的试验数据用于验证优化氮肥制度的结果)。在校准和验证DSSAT模型后,结合DSSAT模型和遗传算法(GA)对长春市20年(1973~1992)气象数据下的玉米氮肥施用制度进行了优化。结果表明,DSSAT模型模拟数据与实测数据之间取得了良好的一致性。优化后的氮肥制度的氮肥施用总量为198 kg/ha,略高于传统氮肥制度(187.5 kg/ha),同时提高了7%~9%的玉米产量和8.4%~12.4%的经济效益。此外,该方法更易于与遥感和气象预测方法相结合,为实时优化农田管理决策提供技术保障(图1)。
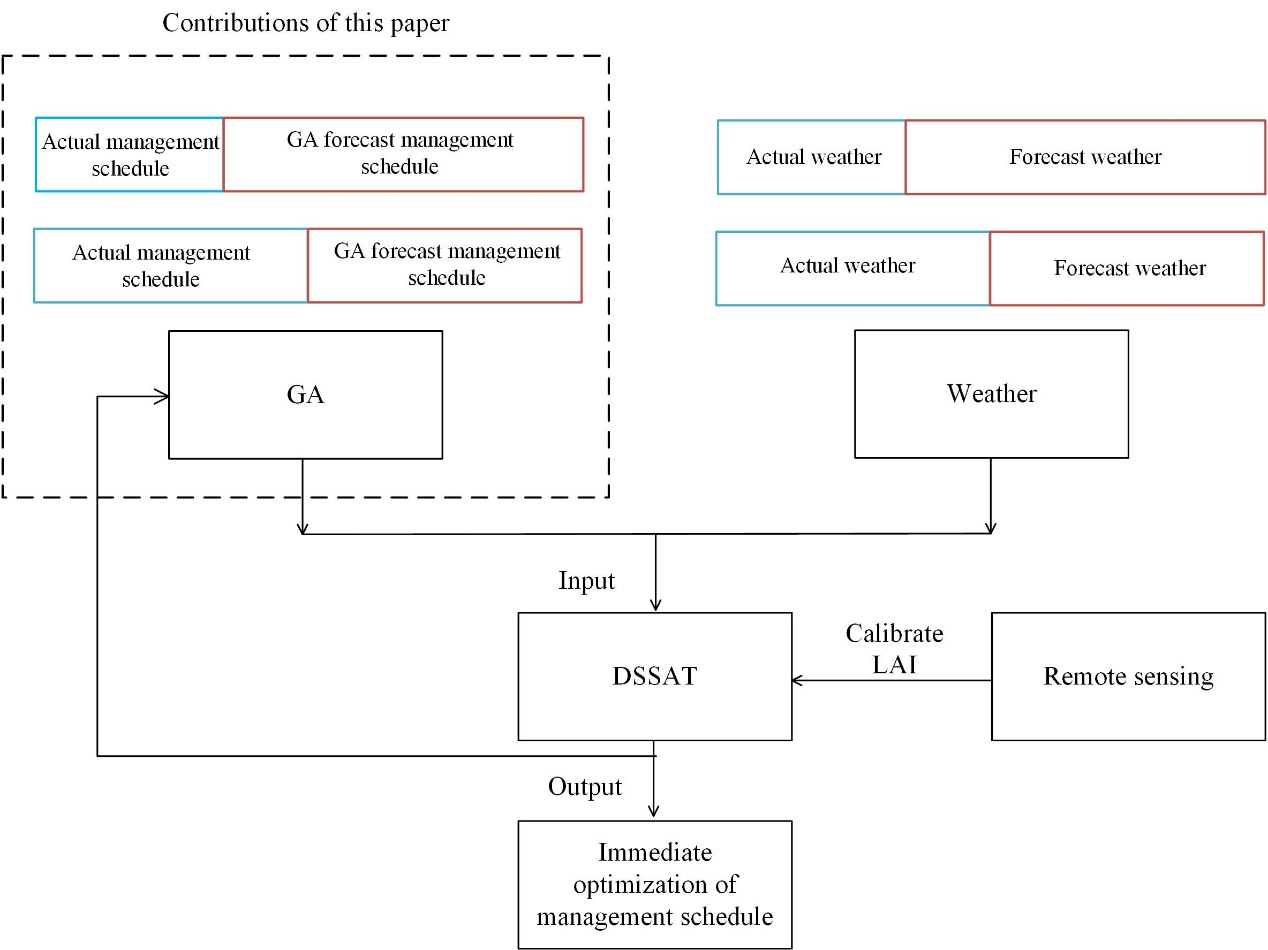
图1.结合气象预测、遥感、作物模型及优化算法的玉米实时田间管理决策模型
参考文献:
Bai, Y., & Cui, H. (2021). An improved vegetation cover and management factor for RUSLE model in prediction of soil erosion. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(17), 21132-21144.
Bai, Y., &Gao, J. (2020). Research on high photosynthetic efficient cultivation with drip irrigation under different mulch of maize. Water Supply, 20(8), 3172-3182.
Bai, Y., Zeng, Y., & Li, Q. (2020).Retaining Performance of Four Types of Drainage Ditch on Phosphorus: Field Work. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 146(11), 04020034.
Gao, J., Bai, Y., Cui, H., & Zhang, Y. (2020). The effect of different crops and slopes on runoff and soil erosion. Water Practice and Technology, 15(3), 773-780.


